Union Find - 并查集
Union-Find算法(并查集算法)是解决动态连通性(Dynamic Conectivity)问题的一种算法,"人以类聚,物以群分"
What is Union Find?
一种用来解决集合查询合并的数据结构,支持 O(1)find, O(1)union
- 查询 Find
- 确定某个元素x属于哪一个集合
- 合并 Union
- 将两个集合合并
应用场景
- Computer Network
- 两个网络节点是否联通
- 最小的布线使得整个网络联通
- Social Network
- Linkedin 两个用户可能认识的人
- 集合论
Union Find vs DFS
在对问题进行建模的时候,我们应该尽量想清楚需要解决的问题是什么! 因为模型中选择的数据结构和算法显然会根据问题的不同而不同!
- Union Find - 给出两个节点,判断它们是否连通,如果连通,不需要给出具体的路径
- DFS - 给出两个节点,判断它们是否连通,如果连通,需要给出具体的路径
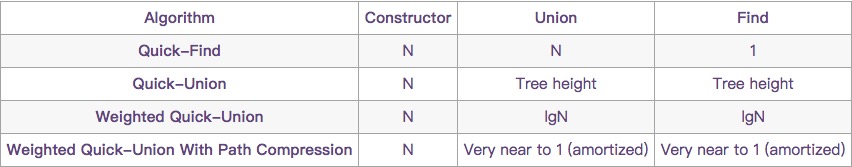
Algorithm
Quick-Find
有点类似于染色的过程,每个节点一个颜色,然后相同的节点设置成相同的颜色。 quick-find算法十分直观符合简单的思考过程。

# Time : O(1)
def find(x):
return root[x]
# Time : O(n)
def union(x, y):
rootx = root[x]
rooty = root[y]
if rootx == rooty:
return
for i in xrange(len(root)):
if root[i] == rootx:
root[i] = rooty
每次添加新路径(Union)就是“牵一发而动全身”,想要解决这个问题,关键就是要提高union方法的效率,让它不再需要遍历整个数组。
Quick-Union
- 以树的思想,表示集合!!!
- 这是UF算法里最关键的思路,以树的形式表示集合,这样组织正好可是很高效的实现find和union!

# Time : O(Tree Height), Worst Case O(n)
# Recursion
def find(x):
if root[x] == x:
return x
return find(root[x])
# Iteration
def find(x):
while root[x] != x:
x = root[x]
return x
# Time : O(Tree Height), Worst Case O(n)
def union(x, y):
rootx = find(x)
rooty = find(y)
if rootx != rooty: 判断两个Element在不在同一个集合当中
root[rootx] = rooty
Weighted Quick-Union
既然树的高度成为制约时间复杂度的瓶颈,我们就想办法让树平衡!
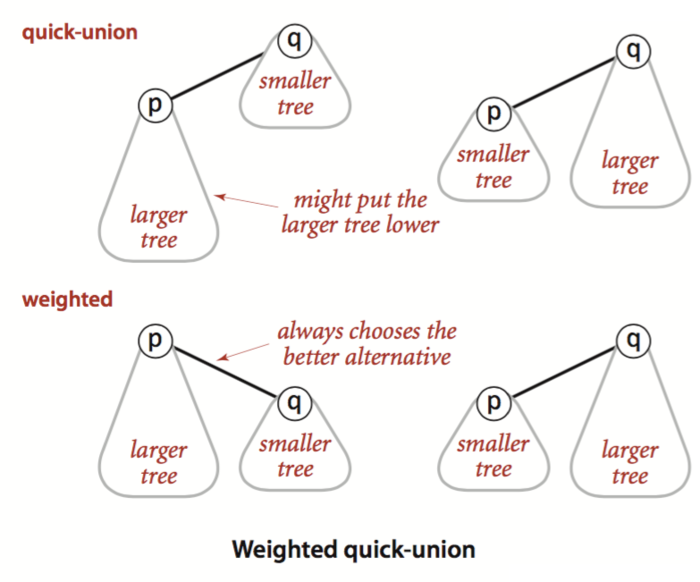
- 以Quick union为基础,我们额外利用一个size[]保存每一个联通集中对象的数量。
- 在调用union()的时候,我们总是把对象数目较少的联通集连接到对象数目较多的联通集中。
- 通过这种方式,我们可以在一定程度上缓解树的高度太大的问题,从而改善Quick union的时间复杂度。
# Time : O(logn)
def find(x):
if root[x] == x:
return x
return find(root[x])
# Time : O(logn)
def union(x, y):
rootx = find(x)
rooty = find(y)
if size[rootx] >= size[rooty]:
root[rooty] = rootx
size[rootx] += size[rooty]
else:
root[rootx] = rooty
size[rooty] += size[rootx]
Path Compression
随着数据的增加,树的深度不断增加,性能会逐渐变差。这个时候,如果我们在计算一个node的root时,将node为根的树摘下来,挂在当前树的根结点上,会降低树的深度,也就是提高效率,降低时间复杂度。
# Path Compression 是在find的过程当中处理的
def find(x):
if root[x] == x:
return x
# make every other node in path point to its grandparent.
root[x] = find(root[x]) # Only one extra line
return root[x]
Weighted Quick-Union With Path Compression
Proof is very difficult, But the algorithm is still simple!
# Weighted 是体现在Union的过程当中
# Time : Very Near to O(1)
def union(x, y):
rootx = find(x)
rooty = find(y)
if size[rootx] >= size[rooty]:
root[rooty] = rootx
size[rootx] += size[rooty]
else:
root[rootx] = rooty
size[rooty] += size[rootx]