Graph 图
LeetCode 上很多问题都可以抽象成 “图” ,比如搜索类问题,树类问题,迷宫问题,矩阵路径问题,等等。Graph 是非常重要而又涵盖很广的内容,以至于有单独的"图论"研究方向。
1 图的计算机表示
- Node / State
- Edge / Action
- Directed vs Undirected graph
- Representation of the graph
Edge List
题目给的Nodes and Edges(Edge List)形式的图
- 要么考虑用Union Find,要么考虑重新建立图的表示
Adjacency Matrix
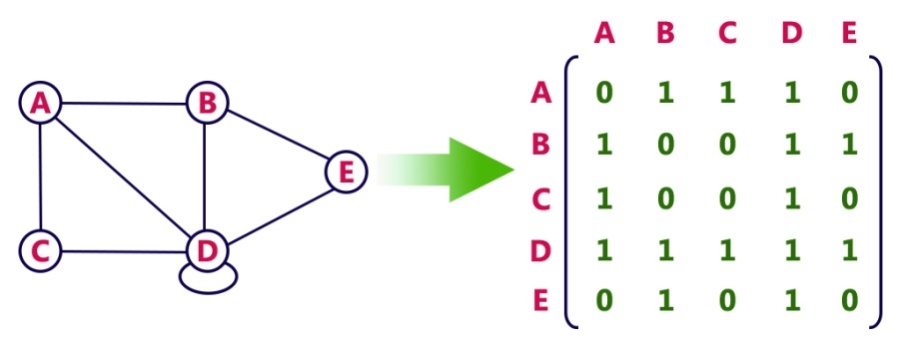
- Pros: Representation is easy to implement. Edge removal takes O(1) time. Queries like whether there is an edge from vertex 'u' to vertec 'v' are efficient and can be done O(1)
- Cons: Consumes more space O(V^2)(V is the number of vertex/node) Even if the graph is sparse(contains less number of edges) == waste of space
Adjacency List
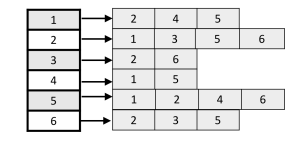 Vertices/Nodes : V, Edges : E
Vertices/Nodes : V, Edges : E
- Pros: Space Complexity = O(V + E). Adding a vertex.node to the graph is easier
- Cons: Time Complexity is O(V) to check wheter there is an edge from a node to the other.(Comprared to O(1) in adjacent matrix)
Adjacency "Hash Set"
用hashset替代list表示相邻的节点,综合了Adjacency Matrix和Adjacency List的优点!
2 Graph Search Algorithm
Breadth First Search
How to describe a BFS's action during an interview?
- Definition 1: expand a node s, 延展一个node
- Definition 2: generate s's neighbor node: reach out to its neighboring node
- Data Structure : Maintain a FIFO queue, put all generated nodes in the queue
- Termination condition : do a loop until the queue is empty
Discussion
- When we deal with the tree-related problem and in the meantime we need to address the relationship on the same level
- BFS is NOT the right algorithm to find the shortest path in the graph
- BFS 的时间空间占用以 branching factor 为底, 到解的距离 d 为指数增长;
- BFS 空间占用上 Queue 是不会像 DFS 一样只存一条路径的,而是从起点出发越扩越大,因此会有空间不够的风险,空间占用为 O(b^d)。
Assume Input - graph adjacency "hash set"
# Undirected Graph
# 其实和Tree的BFS traversal是一样的!
# Why visited array? 如果有环的话需要,没有环的话不需要!
def BFS1():
visited = [0] * n
queue = collections.deque([0])
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
print(node)
visited[node] = 1
for nei in graph[node]:
if visited[nei] == 0:
queue.append(nei)
# Directed Graph
# 从Indegree == 0 的node开始!
def BFS2():
queue = collections.deque([i for i in xrange(n) if indegree[i] == 0])
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
print(node)
for nei in graph[course]:
indegree[nei] -= 1
if indegree[nei] == 0:
queue.append(nei)
Dijkstra's Algorithm
“呆克斯戳” - Best First Search
- Usages: Find the shortest path cost from a single node (source node) to any other nodes in that graph
- Data Structure: Priority Queue (Min Heap)
- Process
- Initial state (start node)
- Node expansion/ Generation rule
- Termination condition 所有点计算完毕也是"Queue is empty"
Properties
- One node can be expanded once and only once
- One node can be generated more than once. (cost can be reduced over time)
- all the cost of the nodes that are expanded are monotonically non-decreasing(所有从 priority queue里面pop出来的元素的值是单调非递减->单调递增)
- time complexity, for a graph with n node and the connectivity of the node is **O(nlogn)**
- when a node is popped out for expansion, **its value is fixed which is equal to the shortest distance from the start node** (非负权重)
Depth First Search
- DFS 的时间占用以 branching factor 为底,树的深度 m 为指数增长
- DFS 的空间占用上,却只是 O(bm),可视化探索过程中只把每个 Node 的所有子节点存在 Stack 上, 探索完了再 pop 出来接着探,因此储存的节点数为 O(bm)。
可以看到无论是 BFS 还是 DFS,树的 branching factor 都是对空间与时间复杂度影响最大的参数;除此之外,BFS 中最重要的是到解的距离,而 DFS 看从当前节点的深度。普遍来讲,DFS 空间上会经济一些,当然也要分情况讨论。
# Undirected Graph
def dfs(node):
visited.add(node)
for nei in node.neighbors:
if nei not in visited:
dfs(nei)
# Directed Graph
visited 需要 三种状态!0-未访问,1-正在访问,2-已经访问
3 Application
133. Clone Graph
克隆Graph,很多graph都是用HashTable一一映射
- Hash Table 新旧node一一映射,再把关系同样映射!
- DFS,BFS都可以把所有node遍历一遍就好
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, node):
if not node:
return None
gmap = {node:UndirectedGraphNode(node.label)}
queue = collections.deque([node])
while queue:
nnode = queue.popleft()
for nei in nnode.neighbors:
if nei not in gmap:
gmap[nei] = UndirectedGraphNode(nei.label)
queue.append(nei)
gmap[nnode].neighbors.append(gmap[nei])
return gmap[node]